Case studies
2019
CLP India contributes to air quality improvement
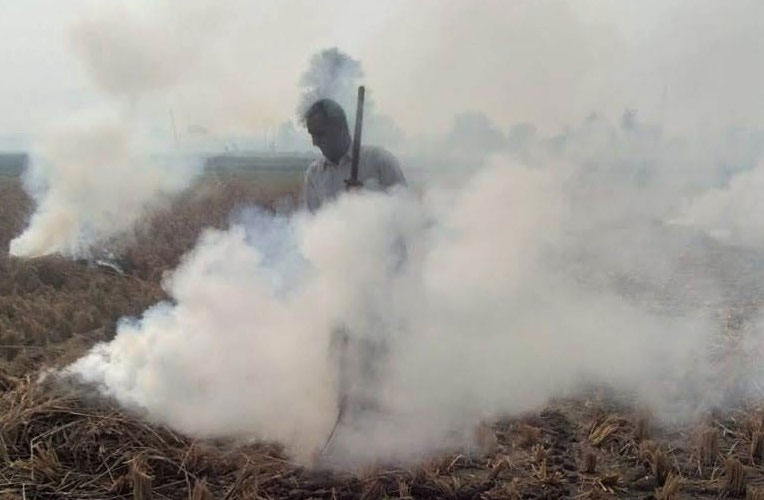
In addition to the emission control projects in the Jhajjar Power Plant, CLP India has partnered with the CII Foundation on a community programme to encourage local farmers to adopt sustainable methods of crop residue management in Haryana.
The two-year project will cover an estimated 9,000 acres of farmland and will initially be implemented in six villages in the districts of Rohtak and Fatehabad in Haryana.
The project is being executed with the help of local non-profit partners and farmer groups. It includes a series of community engagement campaigns to raise awareness and capacity amongst farmers for adopting sustainable and eco-friendly methods of straw management. In the second phase of the project, farmers have been provided with in-situ crop residue management farm tools and technologies for better straw management.
The programme will provide financial support to farmer groups for procuring or hiring high-powered tractors (required for operating in-situ machines) and balers (for clearing straw from the field if there is no scope for in-situ straw management). These machines cut the crop residue, mix them with soil to improve soil health, and plant the seeds for the next batch of crops, thereby saving time, energy and money as compared to conventional methods.
Crop residue burning not only contributes towards harmful emissions, but also depletes essential nutrients from the soil. The project aims to stop crop residue burning in the state, which is a fundamental change in the farming practices in the region, thereby improving the local air quality.
Read more on how CLP India helps tackle air pollution