Supply chain management Copy linkCopied link
Across the Group, procurement and supply chain management are an integral part of business operations. CLP procurement professionals aim to develop and implement effective supply market strategies to acquire quality products and services, reduce supply chain risks, realise Group-wide synergies and deliver optimised supply chain value to stakeholders.
Strategies and procedures
To ensure alignment with business commitments, the CLP Group Procurement Strategy supports these objectives through:
Best practice development through the application of the Group Procurement Standard
Group-level category planning, sourcing and supplier management
Cross-regional delivery support on key projects, supplier engagements and improvement initiatives, and
Federated functional leadership, governance and oversight.
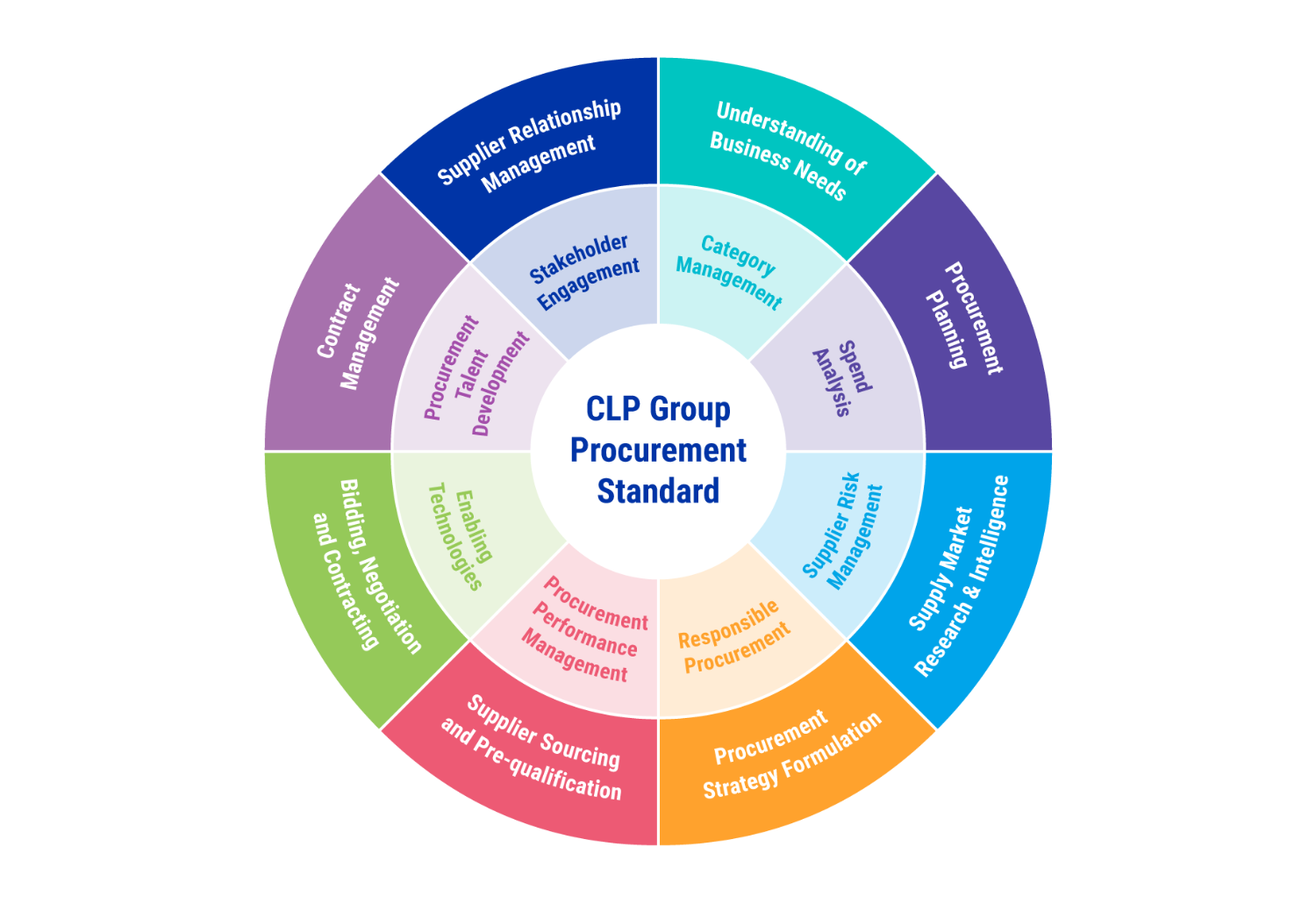
The CLP Group Procurement Standard supports the consistent development of leading practices and capabilities across the Group. It is comprised of 16 “Process” and “Enabler” elements, as illustrated in the figure below and includes responsible procurement, supplier risk management and supplier relationship management.
The CLP Group Procurement Standard
Procurement commitments comply with CLP policies, including:
CLP Procurement Values and Principles, which highlight the procurement department's mission, governance, commitment and strategies
CLP Group Responsible Procurement Policy Statement (RePPS) which highlights the Company's requirements and expectations on suppliers, and
Other procurement policies that govern daily CLP operations.
These day-to-day operations are also guided by CLP’s Whistleblowing Policy and Harassment-Free Workplace Policy. As a trusted partner, CLP encourages suppliers to uphold the applicable principles outlined in these policies.
Procurement is actively involved in supporting category and project steering committees, and to ensure an appropriate level of oversight and governance is applied for procurement decision-making. In addition, procurement commitments are made with reference to clearly defined regional Company Management Authority Manuals.
Monitoring and follow-up
Group Category Councils have been established to oversee aggregated future procurement needs, supply market opportunities and risks, and the development of procurement strategies. Procurement and business units work in close partnership to formulate sourcing strategies and to provide enhanced insights of the supply market. This collaboration has increased CLP’s ability to negotiate and manage risk and supplier relationships, and has resulted in tangible commercial benefits for the businesses.
By following the Group Procurement Standard, businesses across the Group are implementing industry-leading practices in sourcing and supplier management, committing to responsible procurement to build a more sustainable supply chain.
CLP designs fit-for-purpose sourcing strategies to select suppliers who will best meet its requirements and deliver value at an acceptable level of risk. Typically, supplier selections are conducted through competitive tendering and based on an assessment of the supplier’s ability to meet quality, health and safety, environment, delivery, innovation, sustainability and cost requirements. CLP ensures its contracts safeguard stakeholder interests, and reflect suppliers’ commitments and obligations, including legal and regulatory compliance, and the safeguarding of intellectual property rights, data confidentiality and security.
CLP segments the contracted suppliers into tiers. This helps determine the appropriate level of governance and engagement. Segmentation is reviewed annually based on relative contract value and potential business impact, including risks in relation to supply chain and sustainability.
In line with the Corporate Risk Framework, CLP periodically assesses its exposure to strategic supplier risks through heatmaps that reveal the likelihood of failure events and their potential impact on the business. CLP then develops and implements mitigation plans with the suppliers to actively mitigate these risks.
Continuous improvement
CLP has enhanced its Supplier Relationship Management process for strategic suppliers to consistently measure delivery performance, drive continuous improvements and ensure alignment through year-round operational, business and executive reviews.
CLP continues to review past performance, future business needs, as well as technology and innovation roadmaps regularly with suppliers. While supplier performance is measured under a structured framework, suppliers are also invited to provide feedback to CLP. This approach provides candid two-way communication and continuous improvements in the long run. Specific focus on technology roadmaps and innovation will also strengthen CLP for future challenges.
Responsible procurement Copy linkCopied link
These expectations are based on four pillars:
Legal compliance.
Respect for people, including safe working environment, good employment practices, no discrimination, and no use of child labour or forced labour.
Ethics and business conduct, including transparency in business processes, a high standard of business conduct, and no conflicts of interest.
Environmental stewardship, including the efficient use of resources, the responsible disposal of waste, and the monitoring of environmental performance to improve over time.
CLP believes its commitment to continuous improvement, and its ongoing efforts in encouraging others to adopt best practice can create benefits throughout its supply chains. It also builds good corporate citizenship.
Download the Responsible Procurement Policy Statement
In February 2020, EnergyAustralia launched its Supplier Code of Conduct and supplier portal. The Code of Conduct reflects the essence of the Group's RePPS. It includes a whistleblowing service that suppliers may contact directly or anonymously to raise any concerns. The Code of Conduct has been added to contract precedents and EnergyAustralia Purchase Order Terms and Conditions.
Operational responsibilities
CLP contract terms and conditions outline specific sustainability requirements and expectations in terms of business ethics. Suppliers are encouraged to abide by the principles stated in the RePPS and are expected to adopt similar standards and practices when doing business with the Company.
The CLP team leading responsible procurement engages with key internal and external stakeholders to promote procurement practices aimed at reducing environmental, social and governance (ESG) risks and enhancing supplier capabilities to meet CLP’s sustainability requirements.
Strategies and procedures
CLP takes a risk-based approach to implementing responsible procurement across the procurement lifecycle. Sustainability risks are identified and evaluated regularly at category, project and supplier levels against each of the four responsible procurement pillars. This evaluation considers:
Country-specific risks
Product/service-specific risks
Industry/category-specific risks
Legal and regulatory compliance risks
Labour practices and sub-contracting risks
Health and safety risks
Governance and business conduct risks
Environmental risk
Brand and reputational risks.
Specifically, the risk assessment aims to help CLP manage ESG issues, such as labour practices, human rights, modern slavery, child labour, harassment, safety, environment, subcontractor management, and anti-bribery along the value chain. The risk assessment result provides insights into sourcing strategy development for categories and risk mitigation for strategic suppliers.
CLP defines 'critical projects' according to their importance to business operations, ESG risk, and contract value. For these critical projects, suppliers are assessed on their sustainability practices through various tools, including self-declared questionnaires, proposal evaluation, site visits, and where subcontracting is involved, audits on subcontractors’ capability to meet the project's requirements.
Quarterly risk assessments are conducted for strategic suppliers, in conjunction with supplier risk management and supplier relationship management processes. Risk mitigation plans are developed to address identified risks related to delivery performance, supply disruptions and business continuity, and sustainability within the supply chain. Regular meetings with suppliers are conducted to discuss the progress of mitigation plans and explore opportunities for further improvement.
Continuous improvement
Following the publishing of the ISO Guide on Sustainable Procurement (ISO 20400:2017), a review and benchmarking exercise of CLP’s responsible procurement practices against those of other industry leaders were conducted in 2018. In 2019, CLP Power Hong Kong took a pilot role in reviewing the RePPS and developing a future roadmap. The aim is to introduce more definite sustainability requirements on suppliers to further uplift the sustainability capability of suppliers. The requirements include:
A strategic approach to manage sustainability risk
Examining supplier sustainability risk management in supplier selection and supplier relationship management implementation
Analysing sustainability risk for the supplier's location and purchasing categories, and
Monitoring supplier sustainability performance improvement through key performance indicators, periodical site visits, or third-party assessment to assess the sustainability risk.
CLP regularly conducts workshops for contractors to uplift their safety and environmental awareness and capability. To enhance professional development of staff, workshops and training on procurement practices and supplier relationship management are conducted.
These critial projects represented 94% of total procurement projects by value, as compared with 71% in 2019. The increase is attributed mainly to one-off capital projects in Hong Kong.
2020 has been a challenging year due to the COVID-19 pandemic which, amongst the many challenges it presented, disrupted global supply chains. CLP’s multi-regional supply chains remained resilient to these challenges and were able to adapt and provide continuity of supplies across operations. Beyond that, CLP also leveraged on its regional businesses and positive partnerships with suppliers to source supplies of personal protection equipment for its workforce, their families and the community amid a global shortage during the early stages of the outbreak.
Through its Reconciliation Action Plan, developed with Reconciliation Australia, EnergyAustralia made the commitment to increase Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander supplier diversity to support improved economic and social outcomes for the First Nations people of Australia. The Company's membership of Supply Nation, a non-profit organisation that encourages the growth and engagement of Indigenous businesses, helps it to deliver on this commitment. Supply Nation's Sleeping Giant Report found every A$1 spent with an Indigenous business generates A$4.41 of social value through increased employment, training and development opportunities, and investment back into local communities. In 2020, EnergyAustralia spent over A$180,000 with Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander businesses despite the significant impact of the COVID-19 pandemic.
In 2020, the Group sourced products and services from 5,777 suppliers to the total amount of HK$36.5 billion – 95% of this spend was made to local suppliers based in the respective Hong Kong, Mainland China, India and Australia markets. Charts on the number of suppliers by region and the spend per region are shown below.
Number of suppliers by region
Download data (excel)CLP has the highest number of active suppliers in Australia.
Payment to suppliers by region
Download data (excel)The majority of total payments to suppliers in 2020 is shared among the Australia, Mainland China, and Hong Kong markets.
The Group remains committed to responsible procurement practices and proactively engages with suppliers to promote those practices that are key to a sustainable supply chain.
During 2020, for critical project suppliers, the procurement team has:
Assessed 56 strategic suppliers, constituting 56% of the year’s spend, against sustainability requirements.
Confirmed that all strategic suppliers have processes and risk mitigation plans in place to manage risk and continuously uplift their capability. Service providers in Hong Kong for temporary manpower service are assessed on the accuracy and timeliness of temporary manpower pay levels and working hours against CLP requirements.
No significant risk findings related to the CLP Responsible Procurement Policy Statement were identified amongst these strategic suppliers.
EnergyAustralia is required to report under the Australian Modern Slavery Act 2018 and will be submitting their first statement by 30 June 2021. The Company has developed a Modern Slavery Policy which outlines EnergyAustralia’s obligations within our operations and supply chain in relation to modern slavery, and on how those risks will be identified, addressed and assessed.
As part of the development of the report to the Australian Government, a risk matrix was developed of commodities and supplier locations to identify high-risk suppliers to approach, in the first instance, with a survey to obtain a better view of their modern slavery risk. Where suppliers do not have any practices or policies that prohibit child, or forced, bonded or involuntary prison labour, EnergyAustralia is providing those suppliers with tools to develop policies and will be surveying them again in the second half of 2021.
Responsible procurement
Supplier distribution | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Total suppliers by region (number) | 5,777 | 6,362 | 5,721 | 5,536 | 5,248 |
Australia | 2,216 | 2,215 | 1,986 | 1,941 | 1,922 |
Mainland China | 1,142 | 1,166 | 1,011 | 995 | 1,018 |
Hong Kong | 1,013 | 1,000 | 950 | 899 | 721 |
India | 1,134 | 1,704 | 1,476 | 1,443 | 1,366 |
Others (Asia Pacific) | 70 | 77 | 84 | 70 | 65 |
Europe | 121 | 118 | 129 | 112 | 95 |
America | 78 | 77 | 78 | 69 | 54 |
Rest of the world | 3 | 5 | 7 | 7 | 7 |
Payment to suppliers | 2020 | 2019 | 2018 | 2017 | 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Total payment to suppliers by region (HK$M) | 36,544 | 36,746 | 39,183 | 30,868 | 25,972 |
Australia | 8,526 | 8,356 | 9,410 | 7,184 | 4,877 |
Mainland China | 15,577 | 11,603 | 10,339 | 8,343 | 8,872 |
Hong Kong | 8,501 | 8,888 | 8,917 | 7,264 | 6,301 |
India | 1,999 | 3,104 | 4,597 | 2,527 | 2,355 |
Others (Asia Pacific) | 960 | 3,093 | 4,363 | 4,467 | 3,096 |
Europe | 753 | 1,234 | 1,170 | 830 | 415 |
America | 221 | 458 | 380 | 241 | 51 |
Rest of the world | 5 | 10 | 7 | 12 | 5 |